Bevel cost analysis plays a major role. For manufacturers, fabricators, and engineering professionals, understanding the costing of beveling operations is essential for accurate estimation, budgeting, and competitive bidding.
Common industries using beveling include:
- Pressure vessel fabrication
- Pipeline construction
- Shipbuilding
- Heavy machinery manufacturing
- Structural steel fabrication
What Is Material Beveling?
Meaning of beveling: Material beveling is the machining or cutting of a material edge. It is a critical preparatory process used across fabrication industries to create angled edges on metal plates, pipes, and structural components.
Importance of beveling-
- Bevels are used to prepare surfaces for welding. These angled cuts improve weld penetration, reduce defects, and increase the strength and quality of welded joints.
- Remove sharp edges for handling safety, and achieve design aesthetics or functional requirements
Types of Material Bevels
- 1. V-Bevel- A straight-angle bevel used for typical weld preparations (e.g., 30°, 35°, 45°).
- 2. J-Bevel-Curved bevel that reduces filler metal consumption; common in thick plates and piping.
- 3. U-Bevel-Symmetrical curved edges used for high-strength weld joints.
- 4. Compound Bevel-Combination of two angles, often for complex welding requirements.
- 5. Pipe Beveling-Beveling cylindrical components for pipeline welding, often performed using portable beveling machines.
Flow Chart: Costing Process of Material Beveling
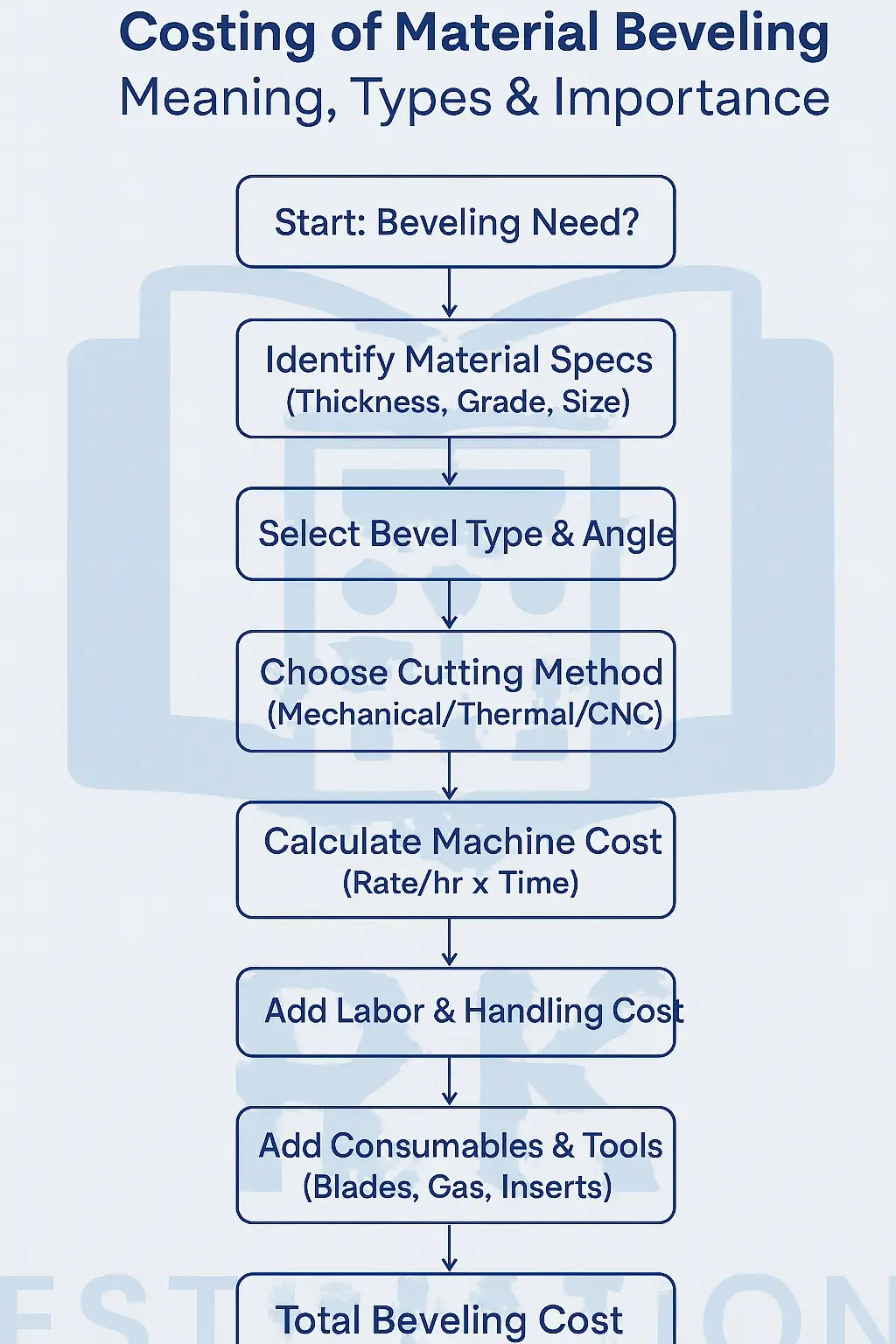
Factors Affecting the Cost of Material Beveling
To prepare accurate estimates, costing must be calculated based on a combination of machine, labor, and material parameters:
1. Material Thickness & Grade: Higher hardness or thickness requires stronger tools and more time.
2. Bevel Type & Angle: Complex bevels (J or U) cost more due to machining difficulty.
3. Cutting Method: Each cutting method has a different operating cost.
- Mechanical beveling (milling, grinding)
- Thermal beveling (plasma, oxy-fuel)
- Automated beveling on CNC machines
4. Labor & Operator Skill: Experienced labor increases precision but adds cost.
5. Equipment Wear & Consumables: Blades, inserts, grinding wheels, and gas consumption impact overall cost.
6. Setup Time & Handling: More handling = higher cost, particularly for large plates or pipes.
Why Costing of Material Beveling Matters
Accurate beveling cost estimation helps in:
- Preparing competitive project quotations
- Reducing unwanted fabrication losses
- Optimizing machine utilization
- Improving weld quality and reducing rework
- Ensuring project profitability