Introduction: In every fabrication or manufacturing project, material cutting is the first and most essential operation. Accurate cutting cost estimation ensures proper budgeting, pricing, and profitability of cutting process of any material Whether it’s a steel plate, pipe, or sheet, cutting defines the dimensions, waste, and overall cost of the project.
 Accurate cutting cost estimation ensures proper budgeting,
pricing, and profitability. Let’s understand what material cutting costing
means, its types, and why it’s crucial in mechanical and structural
fabrication.
Accurate cutting cost estimation ensures proper budgeting,
pricing, and profitability. Let’s understand what material cutting costing
means, its types, and why it’s crucial in mechanical and structural
fabrication. Meaning of Material Cutting Costing
Material cutting costing refers to the process of estimating the total cost involved in cutting raw materials into required shapes and sizes. It includes:
direct costs (gas, electricity, consumables, tools, and labor),
indirect costs (machine depreciation, setup time, handling), and
overheads (maintenance, quality checks).
In simple terms, cutting costing =
(Material Cutting Time × Cutting Rate per Hour) + Consumable + Overheads
Types of Material Cutting Processes
Different cutting methods are used depending on material type, thickness, and accuracy requirements. Each process has its own costing structure.
1. Gas Cutting (Oxy-Acetylene / Oxy-Fuel)
- Suitable for thick mild steel plates.
- Suitable for thick mild steel plates
- Cost depends on oxygen and fuel gas consumption
- Typical rate: ₹10–₹25 per meter (for plates up to 50 mm)
2. Plasma Cutting
- High-speed and precise for MS, SS, and aluminum.
- Cost includes electricity + electrode + gas + operator time
- Typical rate: ₹20–₹50 per meter (depending on thickness)
3. Laser Cutting
- Offers high precision and clean edges
- Best for thin sheets and complex shapes
- Higher machine cost but minimal material waste
- Typical rate: ₹50–₹150 per meter
4. Water Jet Cutting
- No heat-affected zone HAZ); ideal for non-metals or composites
- Cost is based on nozzle wear, abrasive, and water pressure
- Typical rate: ₹80–₹200 per meter
5. Mechanical Cutting (Shearing, Sawing, etc.)
- Economical for straight cuts and mass production
- Cost depends on blade life and machine speed
- Typical rate: ₹5–₹20 per meter
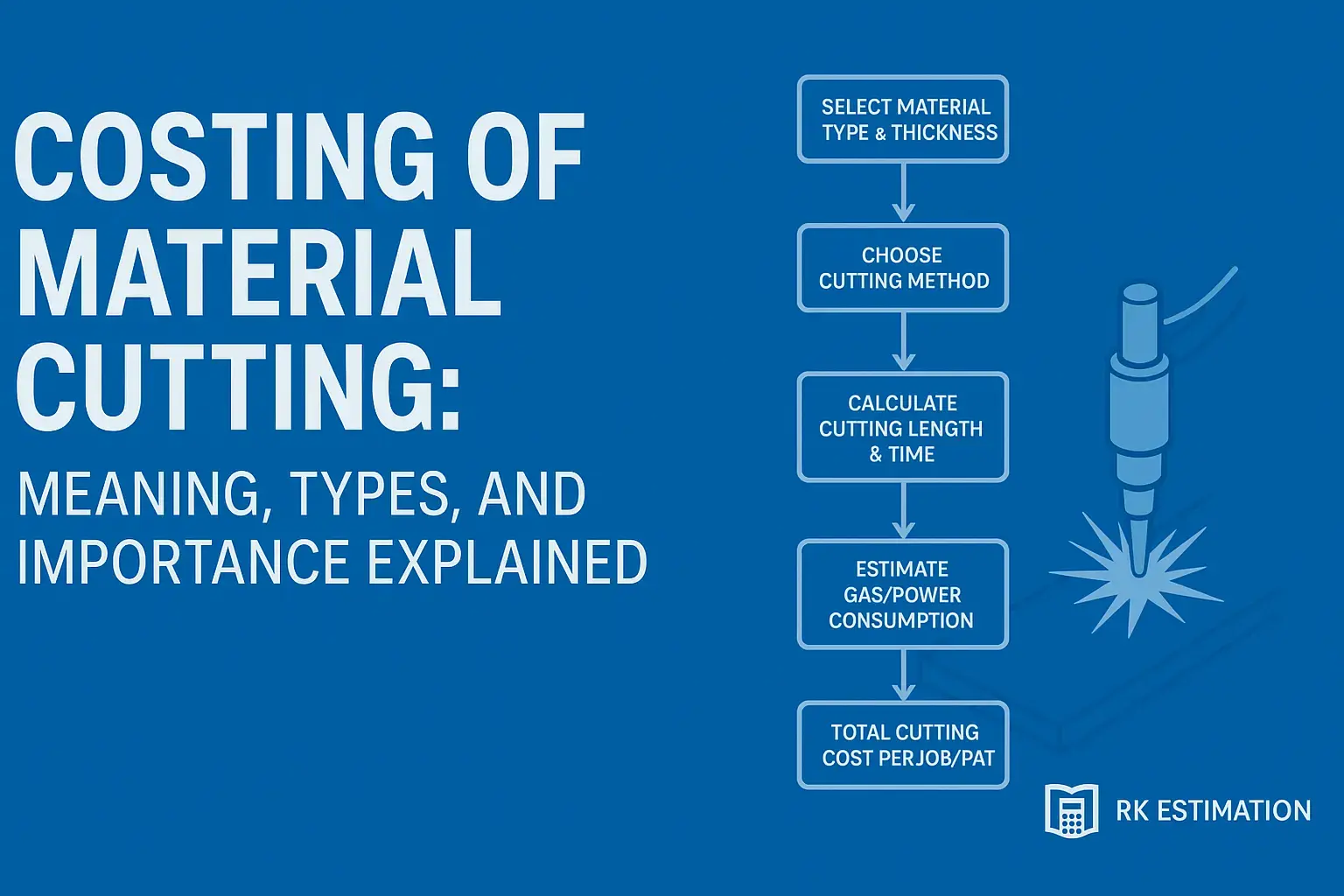
Flow Chart: Costing of Material Cutting Process
Below is a simplified flow to understand how the cutting cost is estimated step by step:
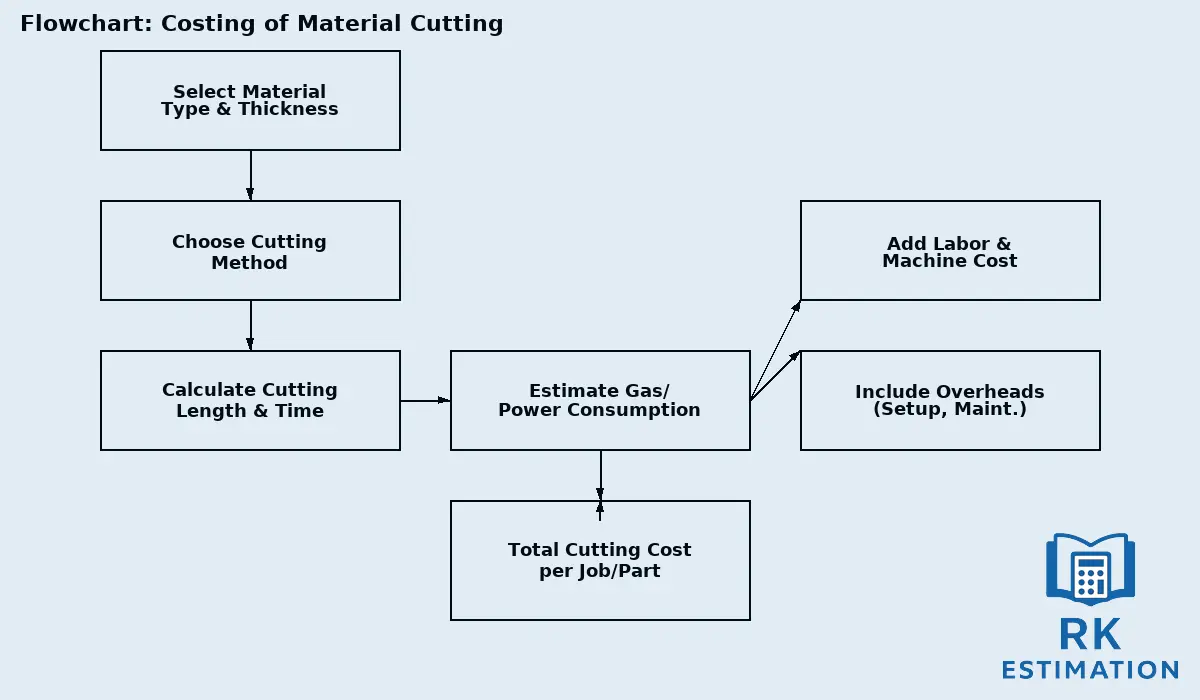
Material Cutting Cost Components
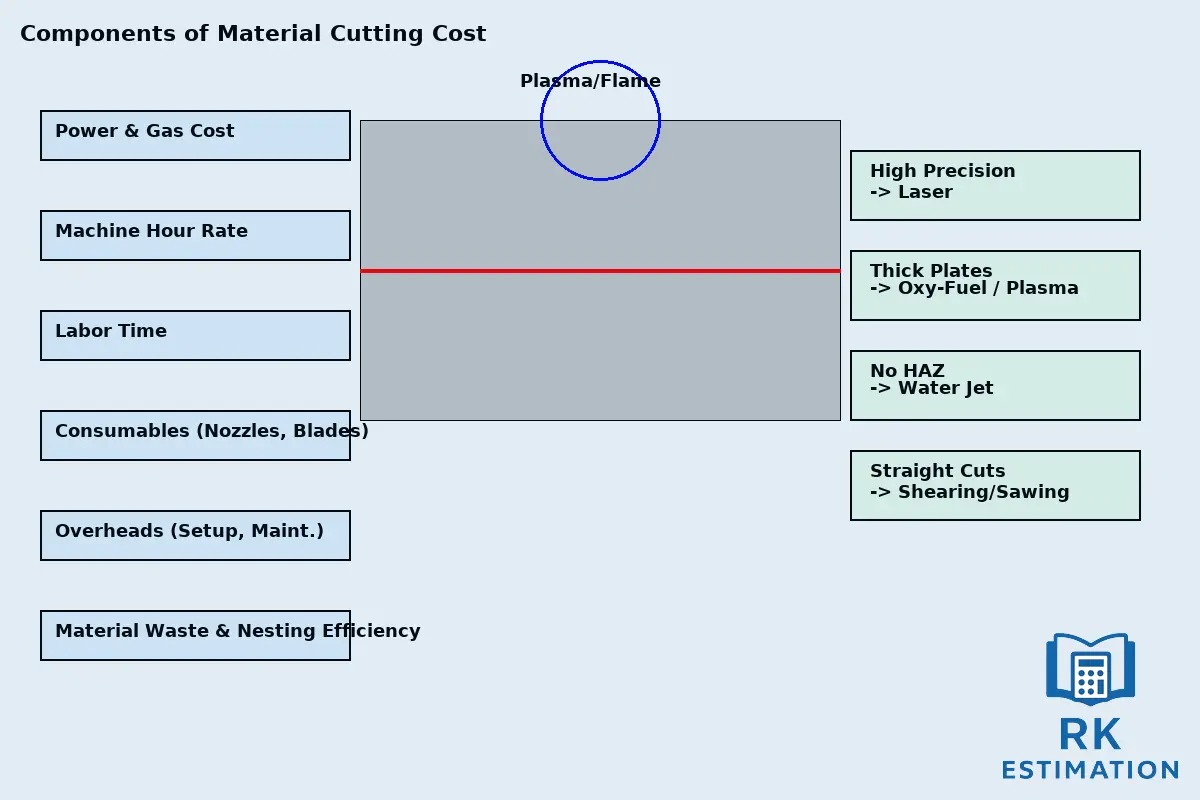
Importance of Material Cutting Costing
| Aspect | Importance |
|---|---|
| Budget Planning | Helps estimate total fabrication cost accurately |
| Pricing Strategy | Enables competitive and profitable quotation |
| Material Optimization | Reduces wastage through accurate layout planning |
| Production Efficiency | Identifies high-cost operations for improvement |
| Client Transparency | Builds trust through data-based costing |
Conclusion
Material cutting may seem like a small step, but in estimation, it’s the foundation of every fabrication project. A precise cutting cost analysis ensures realistic project quotes, better profit margins, and smooth execution.
“Every cut counts — both in accuracy and in cost.”