1. What Is NDT Costing?
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) is a critical quality assurance process used to evaluate materials, welds, and components without damaging them.
In industrial fabrication, infrastructure projects, heavy engineering, and pipeline construction, NDT ensures structural integrity and compliance with codes.
NDT costing refers to estimating the total expenses involved in performing these tests, including labour, equipment, consumables, site conditions, and documentation.
Accurate NDT costing helps contractors, fabricators, and QA teams plan budgets effectively, manage resources, and price projects competitively.

2. Types of NDT Processes Affecting Cost
Different NDT methods require different equipment, skills, consumables, and safety measures — all of which influence the final cost.

a) Visual Testing (VT)
- Basic & low-cost inspection
- Minimal equipment required
- Ideal for weld appearance checks
b) Radiographic Testing (RT)
- Uses X-ray or gamma radiation
- High equipment & safety compliance cost
- Expensive consumables (film / digital imaging)
c) Ultrasonic Testing (UT)
- Uses high-frequency sound waves
- Equipment cost is moderate to high
- Requires skilled & certified technicians
d) Magnetic Particle Testing (MPT)
- Detects surface/subsurface defects in ferromagnetic metals
- Low consumable cost, moderate equipment cost
e) Dye Penetrant Testing (DPT / PT)
- Surface crack detection on non-porous materials
- Low-equipment, low-consuming testing method
f) Eddy Current Testing (ECT)
- Used for welds, heat exchangers & aerospace parts
- High equipment cost, technician certification required
3. Key Elements in NDT Cost Calculation

1. Technician Labour Cost
- Hourly rate of Level I, II, or III inspectors
- Setup time + actual testing time + reporting time
2. Equipment & Machine Cost
- Depreciation cost of RT, UT, MPI, or ECT machines
- Calibration & annual certification
- Repair & maintenance
- Accessory cost (cables, probes, sensors, film,
gamma sources)
3. Consumables
Includes consumable materials used during the testing
- Film, chemicals, indicators
- Penetrant, cleaner, developer (DPT)
- Couplant gels (UT)
- MPI powders, sprays
4. Compliance & Radiation Safety Cost (RT only)
- Lead shielding
- Radiation officer requirement
- Film processing room
- Regulatory approvals
5. Joint Preparation & Accessibility
- Surface cleaning
- Grinding or polishing
- Scaffolding or height access (if required)
6. Power Consumption
- Equipment power usage for UT, MPI, or RT sets
7. Reporting & Documentation Cost
- Preparation of reports, records, images, and acceptance notes
- Third-party or client approval steps
8. Travel, Mobilization & Site Conditions
- Cost of mobilizing technicians & machines
- Remote site or hazardous area allowances
4. How to Prepare a Cost Estimate for NDT
Steps to Prepare a Cost Estimate for NDT:
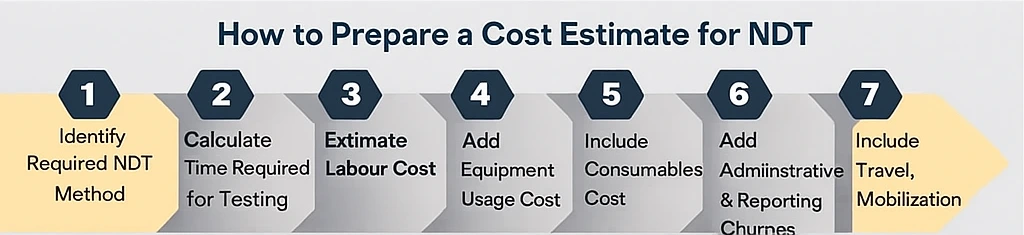
Step 1: Identify the Required NDT Method
Based on welding procedure, material thickness, joint type, and project specification.
Step 2: Calculate Time Required for Testing
- Preparatory time
- Testing time per joint, per meter, or per component
- Reporting time
Step 3: Estimate Labour Cost
Labour Cost = Technician Rate × Total Time (hours)
Step 4: Add Equipment Usage Cost
Include depreciation, calibration, maintenance, and rental (if applicable).
Step 5: Include Consumables Cost
Sum of all consumables used per test.
Step 6: Add Compliance & Safety Charges (mainly for RT)
Step 7: Add Administrative & Reporting Charges
Step 8: Include Travel, Mobilization & Overheads
Final Cost Formula:
Total NDT Cost = Labour + Equipment Cost + Consumables + Compliance
Cost + Reporting + Overheads + Margin
5. Factors That Influence Total NDT Cost
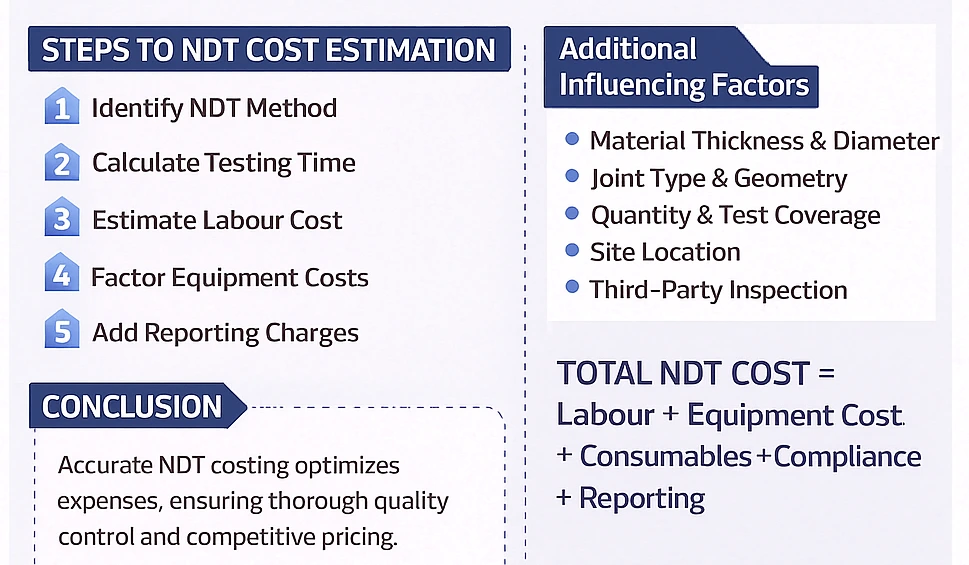
1. Material Thickness & Diameter
Thicker materials require more exposure time or deeper penetration.
2. Joint Type & Geometry
Complex welds increase testing time and setup.
3. Quantity & Coverage
More tests = better distribution of fixed costs.
4. Customer Specification & Code Requirements
More stringent acceptance criteria often increase cost.
5. Site Location & Accessibility
Remote locations require additional mobilization charges.
6. Third-Party Inspection Requirement
Adds cost due to coordination and additional time.
6. Conclusion
The cost of Non-Destructive Testing depends on method selection, technician skills, equipment usage, consumables, site accessibility, and reporting requirements.
A
structured NDT costing approach helps fabricators, contractors, and QA/QC
professionals achieve accurate estimates, control expenses, and ensure quality
without unnecessary overspending