Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) are essential pillars in manufacturing, fabrication, construction, and engineering.
While quality processes ensure that products meet required standards, they also involve measurable costs that organizations must understand to maintain competitiveness.
In this blog, we explore what QA/QC truly means, how the process works and the key cost factors that influence overall project pricing.
What Is the QA/QC Process?
The QA/QC process is a structured system that ensures a product, weld, material, or component meets defined quality requirements.
Quality Assurance (QA) focuses on establishing systems, procedures, and preventive measures.
Quality Control (QC) ensures the final output meets specifications through inspection, measurement, and testing.
Together, QA/QC minimizes defects, reduces rework, enhances reliability, and ensures compliance with industry standards such as ISO, ASME, ASTM, AWS, and client-specific specifications.
Meaning of QA/QC Costing
QA/QC costing refers to calculating all the expenses associated with quality-related activities including:
- Planning
- Executing
- Monitoring
- Inspecting and
- Documenting.
These costs directly influence the total project cost and must be considered during estimation and bidding.
Methods Used in QA/QC
- Incoming Material Inspection
- In-Process Inspection
- Final Inspection
Proper costing of QA/QC Process helps companies:
- Allocate resources efficiently
- Avoid unexpected inspection expenses
- Improve accuracy during estimation
- Reduce quality-related failures
- Maintain compliance and client trust
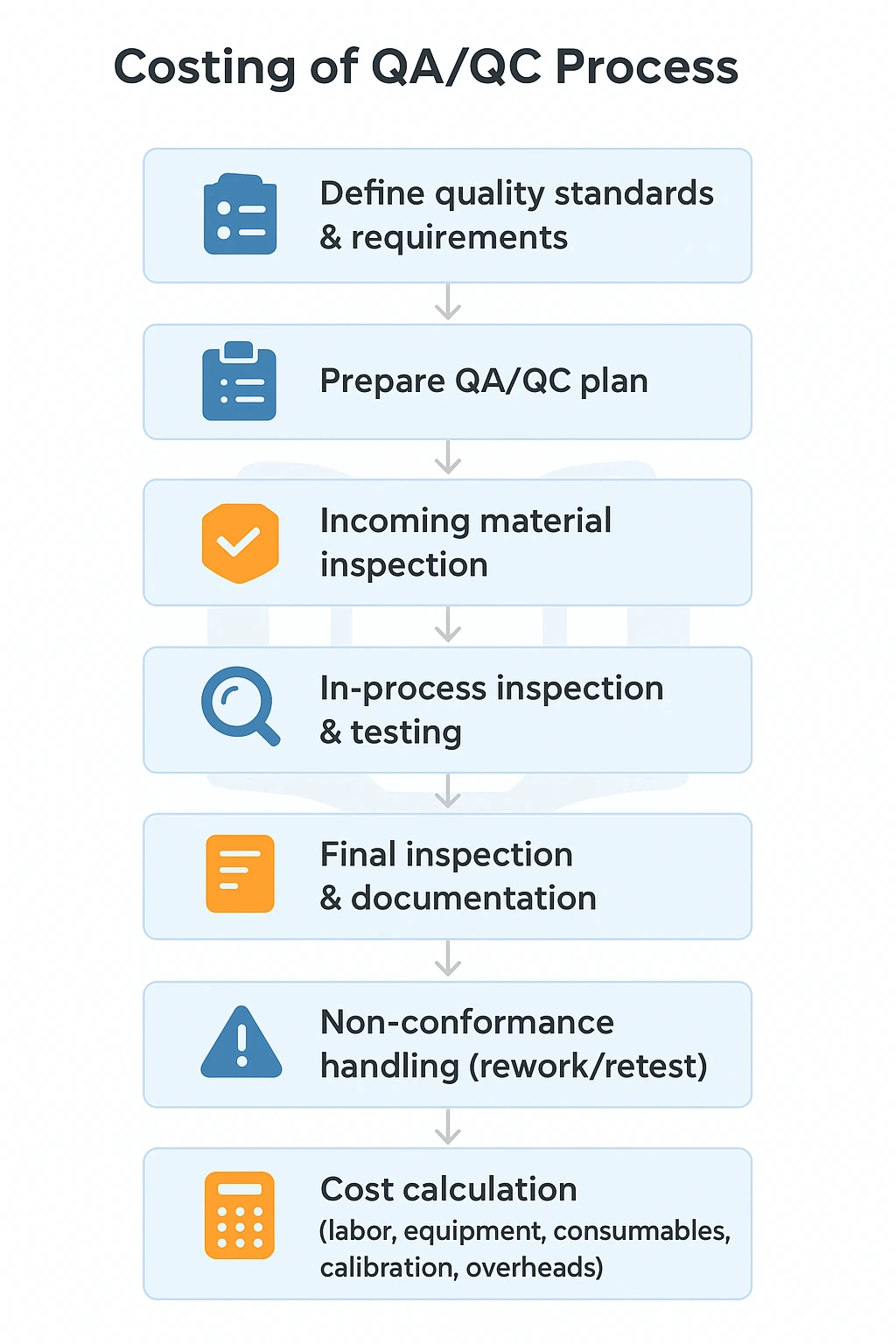
Step-by-Step QA/QC Workflow in Costing
- Define quality standards & requirements
- Prepare QA/QC plan
- Conduct incoming material inspection
- Perform in-process inspection & testing
- Conduct final inspection
- Handle non-conformance (rework/retest)
- Prepare reporting & quality documentation
- Calculate total QA/QC cost (labor, equipment, consumables, calibration, overheads)
1. Define Quality Standards & Requirements:
Below are the Main Steps to Define Quality Standards & Requirements:
- Review client specs
- Identify codes & standards
- Define product/process criteria
- Convert requirements into measurable parameters
- Align with design
- Conduct risk analysis
- Define ITP requirements
- Document standards
- Align with vendors
- Review & approve
- Train teams
- Monitor & revise
2. Prepare QA/QC plan:
Below is a complete step-by-step method to prepare an effective QA/QC Plan.
- Understand Project Requirements
- Define Quality Objectives
- Define Project QA/QC Organization & Responsibilities
- Establish Required Procedures & Inspection Plans
- Prepare Inspection & Test Plan (ITP)
- Define Material Control & Traceability
- Define Calibration & Equipment Control
- Risk Assessment & Control Measures
- Define Testing Requirements
- Document Control & Record Management
- NCR & Corrective Action System
- Training & Competency Requirements
- Final Documentation & Quality Dossier
3. Conduct incoming material inspection
All raw materials and purchased components are inspected for compliance with
- Technical specifications
- Test reports and certificate
- Inspection checklists
- Traceability records etc.
4. Perform in-process inspection & testing
Inspection and testing performed during production, machining, welding, fabrication, painting, or assembly to ensure continuous compliance.
Includes NDT methods such as: Visual Testing (VT), Radiographic Testing (RT), Ultrasonic Testing (UT), Magnetic Particle Testing (MT), Dye Penetrant Testing (DPT), Eddy Current Testing (ECT)

5. Conduct final inspection
Dimensional verification, functional tests, pressure tests, and documentation review before dispatch.
6. Handle non-conformance (rework/retest)
A Non-Conformance (NC) occurs when materials, workmanship, processes, or documentation do not meet specified requirements.
An effective
NCR (Non-Conformance Report) handling system ensures quality, traceability, and
corrective action.
7. Prepare reporting & quality documentation
Quality documents and Records include- Test reports, inspection checklists, calibration certificates, and traceability records are compiled and maintained as part of final project documentation.
Key Cost Factors in QA/QC Process
QA/QC costing includes multiple direct and indirect cost components:
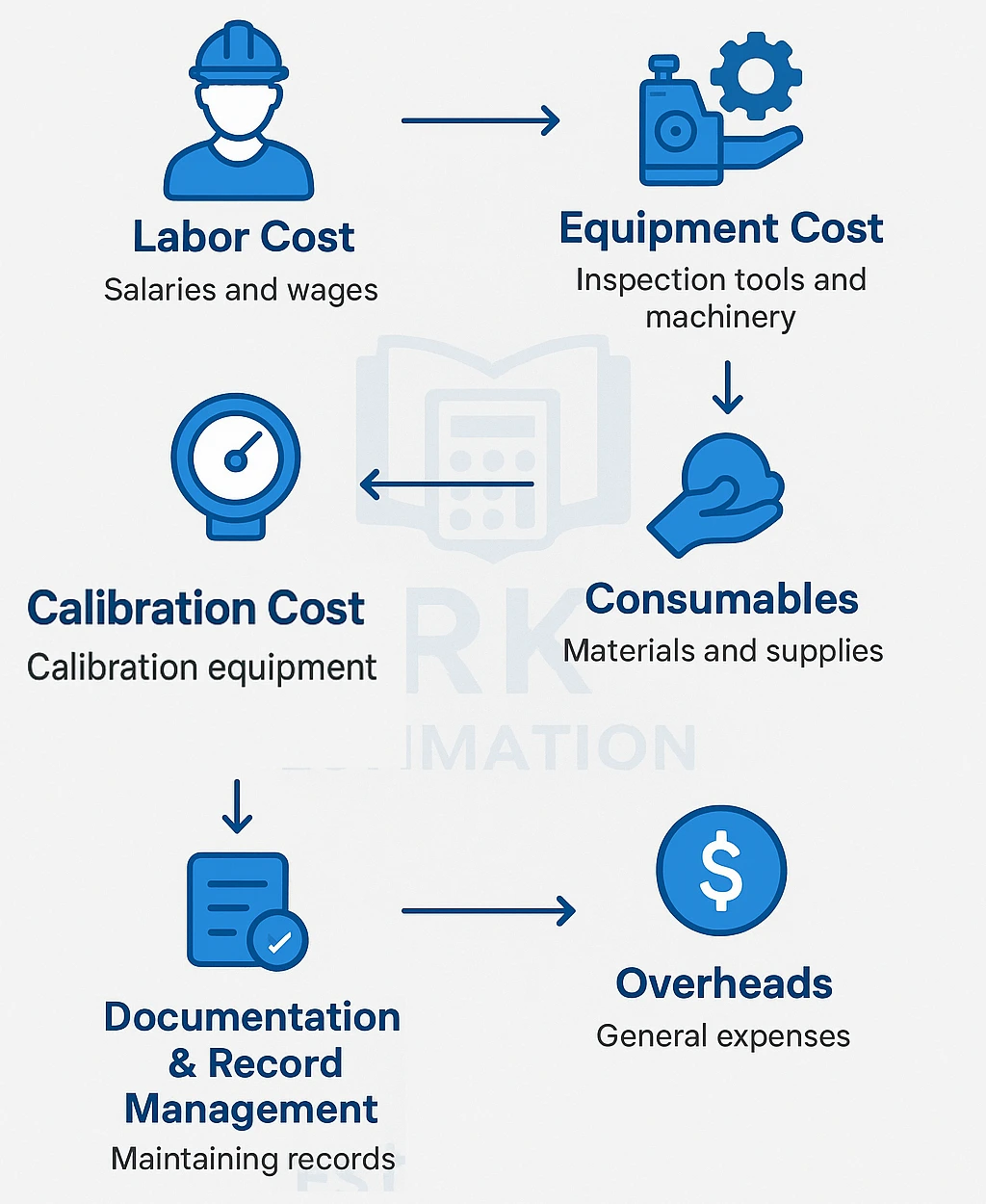
Below are the main Key Cost Factors in QA/QC Process:
1. Labor Cost
- QA engineers and inspectors
- NDT technicians
- Quality supervisors
- Documentation & reporting staff
Costs depend on skill level, certifications, and project duration.
2. Equipment Cost
- NDT instruments (UT machines, MPI yokes, DPT kits)
- Measuring tools (micrometers, gauges, calipers)
- Testing machines (load testing, hardness testers)
Depreciation and maintenance also contribute.
3. Consumables
- DPT chemicals
- MPI powders
- Cleaning agents
- Reporting stationery
These recurring items add to inspection cost.
4. Calibration Cost
All inspection and testing instruments must be periodically calibrated to maintain accuracy.
Calibration agencies charge based on the instrument type and certification requirements.
5. Documentation & Record Management
Preparation of:
- ITPs (Inspection and Test Plans)
- QAP (Quality Assurance Plan)
- Final dossiers
- Material certificates
- Traceability reports
Documentation can consume significant time and labor resources.
6. Overheads
Includes administrative and indirect costs:
- QA software or ERP tools
- Training and certification (ISO, AWS, ASNT)
- Third-party inspection fees
- Travel & site inspection expenses
Why Accurate QA/QC Costing Matters
Accurate QA/QC costing allows organizations to:
- Submit competitive and profitable bids
- Avoid hidden inspection expenses
- Ensure compliance without overspending
- Reduce rejection and rework costs
- Deliver reliable, high-quality products
Including detailed QA/QC costing in your project estimate ensures transparency and boosts client confidence.
Conclusion
The QA/QC process is an integral part of any engineering or manufacturing project, and its cost must be carefully calculated. By understanding each step—standards, inspection, testing, documentation, and evaluation—you can create more accurate estimates and achieve better project outcomes.