In any supply chain or industrial operation, logistics cost plays a critical role in determining total operational expenses and product pricing.
Understanding how to calculate logistics cost helps companies
improve profitability, optimize transportation, reduce wastage and strengthen
efficiency.
This blog explains the meaning of logistics costing, different costing methods and the key cost components involved in logistics operations.
What is Logistics Costing?
Logistics costing is the process of identifying, calculating and managing all costs involved in the movement, storage and handling of goods from the supplier to the final customer.

It includes expenses related to:
- Transportation
- Warehousing & Storage
- Inventory Management
- Packaging
- Administrative and Operational activities
The objective is to control costs, reduce inefficiencies and ensure timely delivery.
Why Logistics Costing is Important
- Helps reduce transportation and warehousing expenses
- Improves delivery speed and reliability
- Enhances profit margins
- Supports strategic decision-making
- Helps identify inefficient or high-cost supply chain activities
Methods of Logistics Costing
Below are the main methods to calculate Logistics Costing:

1. Activity-Based Costing (ABC)
This method allocates costs based on actual activities performed in the logistics chain. Example: cost per trip, cost per pick, cost per inventory movement.
Best for: companies wanting detailed visibility into individual logistics activities.
2. Standard Costing
Uses predetermined, fixed cost values for transportation, handling and warehousing based on historical data.
Best for: budgeting, forecasting and performance comparison.
3. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
This method calculates the total lifetime cost of logistics operations, including hidden costs such as delays, damages, risks and inefficiencies.
Best for: long-term strategic logistics planning.
4. Cost-Per-Unit Method
Calculates logistics cost per unit, per kilometer, per ton, per pallet, or per container.
Best for: manufacturing, distribution, export operations.
5. Landed Cost Method
Calculates the total cost to bring a product to its destination, this is the best for: method for import/export businesses.
Landed cost method including:
- freight
- customs duties
- taxes
- insurance
- handling charges
How to Calculate Landed Material Cost: Click below Button:
How to Calculate Material Cost (Step-by-Step Guide).
Key Cost Factors in the Logistic Process
Below are the Key Cost Factors in the Logistic Process:
Let's discuss each Cost Factors in the Logistic Process:
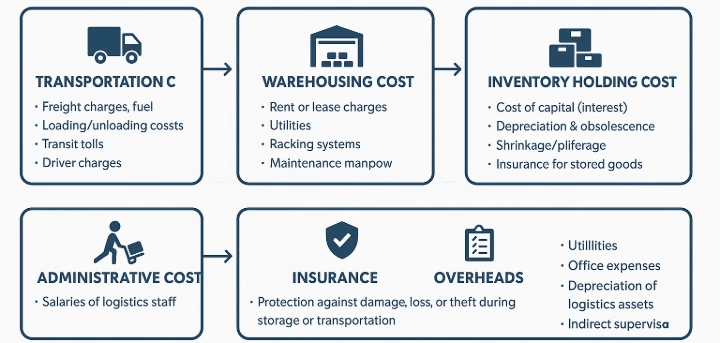
1. Transportation Cost
Transportation cost is the total expense of moving materials, equipment or goods from one location to another.
Transportation cost is the largest component of logistics costing. Includes:
- fuel cost
- driver wages
- vehicle maintenance
- tolls & permits
- freight charges
- container & shipping charges (air/sea/road)
Transportation Cost Explained: Meaning, Types, Importance and Key Cost Factors: Click below Button:
2. Warehousing & Storage Cost
Includes the expenses for storing goods:
- warehouse rent
- utilities (electricity, temperature control)
- equipment (forklifts, racks)
- security systems
- software/automation systems
3. Inventory Holding Cost
Costs associated with keeping stock:
- capital cost (blocked cash)
- insurance
- depreciation
- spoilage, damage, obsolescence
4. Handling & Packaging Cost
Expenses related to loading, unloading, picking, packing and labeling, including:
- labor cost
- packaging materials
- pallets, crates, strapping
- automated machinery cost
5. Administrative & Documentation Cost
Includes:
- logistics management software
- communication and coordination
- documentation & compliance
- customs paperwork
- office overheads
6. Insurance & Risk Management Cost
Covers costs for protection against loss or damage during transit:
- cargo insurance
- in-transit risk coverage
- warehouse insurance
7. Overheads & Miscellaneous Costs
Additional logistics-related expenses:
- technology systems (ERP/WMS/TMS)
- training
- audits
- emergency shipments
- delays and penalties
How to Calculate the Total Cost of Logistics
To calculate the Total Cost of Logistics, below formula can be used:
Total Logistics Cost = Transportation Cost + Warehousing
Cost + Inventory Holding Cost + Handling Cost + Administrative Cost + Insurance
+ Overheads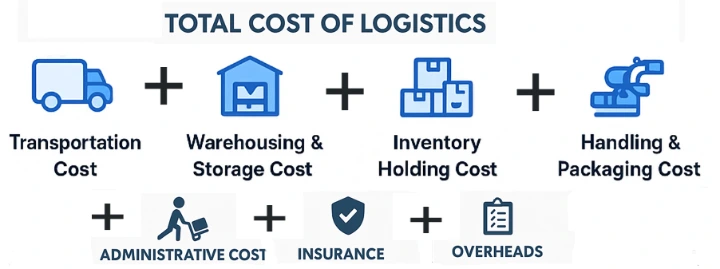
You can also calculate logistics cost per unit, per km, or per shipment depending on your requirement.
Conclusion
A well-planned logistics costing system helps businesses reduce supply chain expenses and boost operational efficiency.
By analyzing transportation, warehousing, inventory, and administrative costs, you can identify savings opportunities and improve overall performance.