Welding plays a crucial role in almost every fabrication and manufacturing project—from small components to large industrial structures.
As welding directly influences material consumption, man-hours, quality, and safety, understanding its cost structure is essential for accurate project estimation.
This blog breaks down what welding costing means, how different welding types affect cost, and why it is important for project success.
What is Welding Costing?
Welding costing is the process of calculating the total expenses involved in completing a welding operation.
It includes direct and indirect cost factors such as labor time, welding consumables, equipment usage, electricity consumption, joint preparation, quality testing, and overheads.
The goal is to forecast the true cost of welding before production begins, ensuring optimal planning and budgeting.
Types of Welding and Their Cost Impact
Different welding processes come with different skill requirements, equipment costs, filler materials, and energy demands.
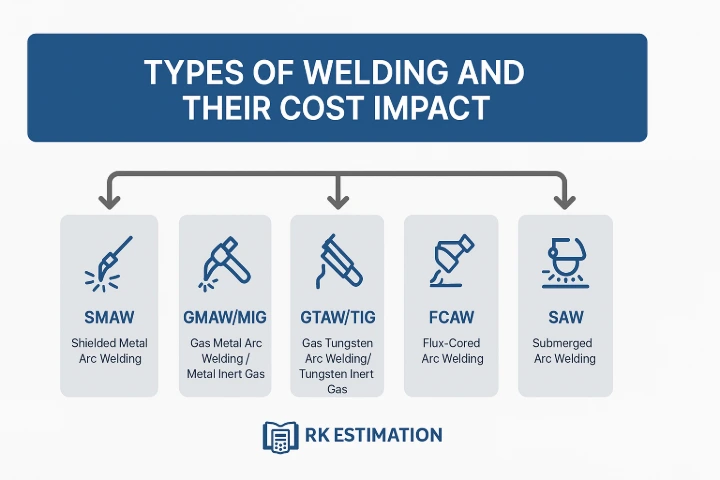
Each welding type affects cost differently based on deposition rate, efficiency, consumables, and manpower. Common types include:
1. Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
- Moderate equipment cost
- Higher consumable usage (electrodes)
- Skilled labor required
2. Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW/MIG)
- Higher machine cost
- Faster welding speed → lower labor cost
- Ideal for repetitive or large-scale fabrication
Costing of GMAW (MIG Welding): Meaning, Types, Importance & Key Cost Factors Explained: Click below Botton
3. Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW/TIG)
- Highest skill level
- Slower process → higher man-hour cost
- Used for high-precision or thin materials
4. Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
- High deposition rate → efficient for heavy structures
- Higher wire cost but lower total job time
5. Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)
- Excellent for long, continuous welds
- High productivity but requires specialized equipment
Key Elements in Welding Cost Calculation
A complete welding cost breakdown usually includes:
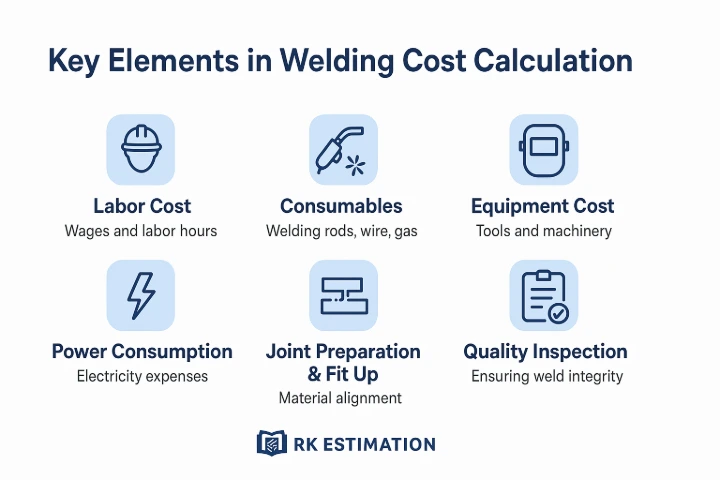
1. Labor Cost
- Welders’ skill level
- Welding speed (WPS-based)
- Setup and idle time
2. Consumables
- Electrodes, wires, shielding gas
- Flux, filler materials
- Consumable wastage %
3. Equipment Cost
- Machine depreciation
- Maintenance
- Accessories (torches, cables, nozzles)
4. Power Consumption
- Current and voltage
- Welding duration
5. Joint Preparation & Fit-Up
- Cutting, beveling, edge quality
- Tack welding
6. Quality Inspection
- Visual test (VT)
- NDT methods like UT, RT, MT, PT
- Repairs and rework
Importance of Welding Costing in Fabrication Projects
Welding costing is vital for:
✔ Accurate Project Estimation
Prevents underquoting and ensures profitability.
✔ Material & Consumable Optimization
Helps reduce wastage and achieve efficient usage
✔ Selecting the Right Welding Process
Comparing process cost helps in choosing the best-fit method.
✔ Improving Overall Productivity
Clear estimation avoids delays and bottlenecks.
✔ Quality Assurance & Compliance
Ensures inspection costs are included to meet standards such as AWS, ASME, and ISO.
Conclusion
Welding costing is more than just calculating consumables or labor—it’s a comprehensive approach to managing efficiency, quality, and profitability. Whether you're designing a fabrication project, preparing a cost estimate, or optimizing your production line, a deeper understanding of welding cost factors helps in making informed decisions.